Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
In brief
The robotics is a field of computer science and engineering concerned with creating robots, devices that can
move and react to sensory input. Robotics is one branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI), which is concerned
with producing machines to automate tasks requiring intelligent behavior, e.g. motion control, planning and
scheduling, the ability to answer diagnostic and consumer questions, handwriting, speech and facial
recognition.
Conventional AI, also known as symbolic or logical AI, mostly involves methods classified as machine
learning, characterized by formalism and statistical analysis, like expert systems, case based reasoning,
bayesian networks and behavior based systems.
A different school of thought, known as Computational Intelligence (CI), involves iterative development or
learning (e.g. parameter tuning in connectionist systems). Learning is based on empirical data and is
often associated with soft computing. Methods mainly include neural networks, fuzzy systems, evolutionary
computation. In other words, typical AI techniques are top-bottom, i.e. the structure of models and solutions
is imposed from above. On the contrary, CI techniques are generally bottom-up, where order
and structure emerge from an unstructured beginning.
Topics
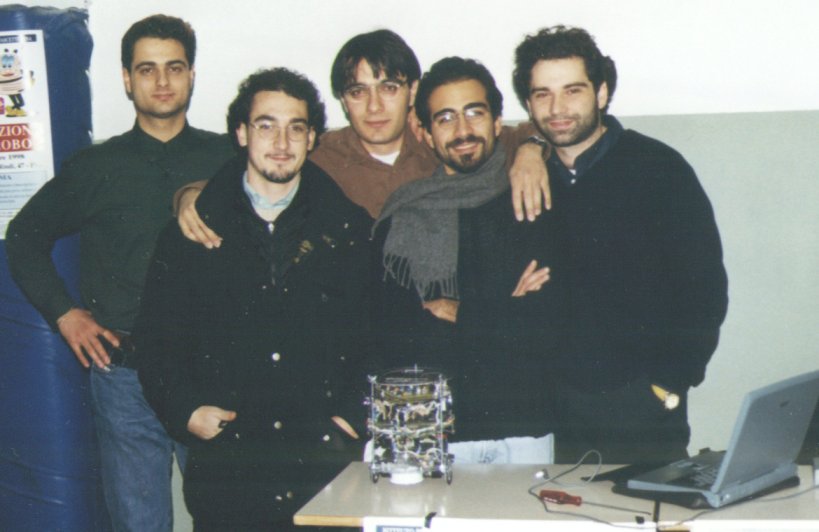
The PIC3 mini-robot was designed by Mario G.C.A. Cimino during his academic studies, under the support of Prof. M. Avvenuti and Prof. A. Balestrino. In order to accomplish in a short time the implementation of a propotipe, he set up the Machine Intelligence Team (M.I.T.) with other four academic students: A. Campana (computer scientist), E. Campanelli (physicist), P. Imbesi and L. Piccinini (electronics engineers). The robot can autonomously move inside an arbitrary-shaped maze, exploiting a set of sensors and actuators for exploring and identifying three types of source: sound, light and gas. The central control unit is a Microchip PIC16F84 controller.
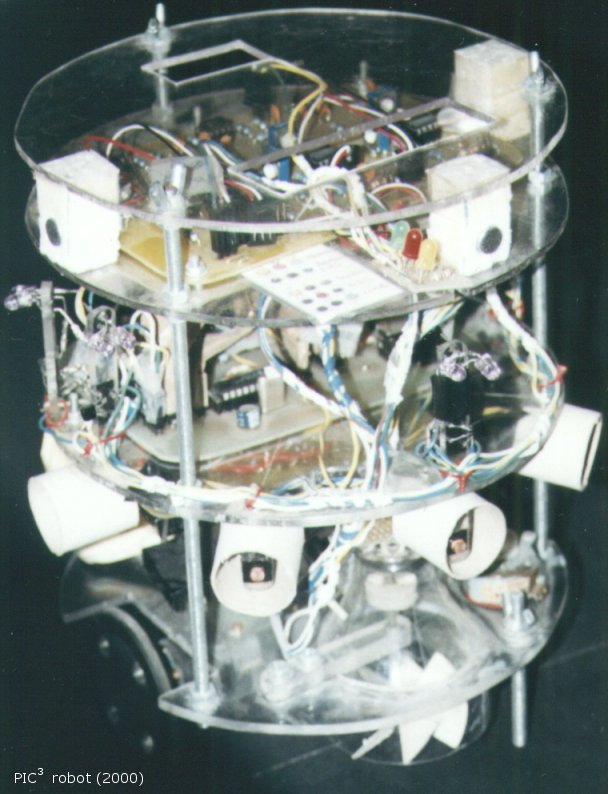
The PIC3 mini-robot
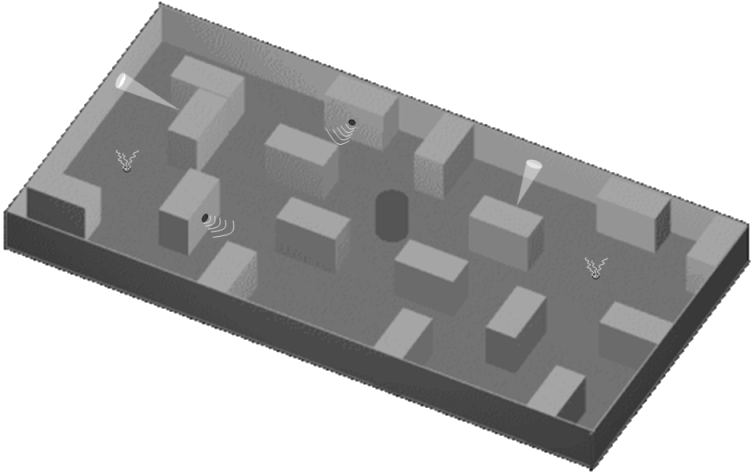
A model of the competition maze
